Teigo Iba’s personality
“Yuo,” a biography of Teigo Iba published in 1933, describes his philosophy and personality in detail. The book mentions that in 1907, Iba’s friend Kinichi Kawakami*1 urged Shigeru Yoshida, his junior at the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and consul-general in Mukden, to meet Iba. In setting up the meeting, it was not Kawakami’s intention that Iba and Yoshida would discuss current affairs or the situation in China, but rather that Yoshida would benefit from encountering such a thoroughly admirable man: “I am sure you will find Iba warmhearted. He is like a breeze in the spring. If you aspire to be a leader in the future, such attributes will be of great advantage to you.” Yoshida, who subsequently served as prime minister and charted the course of Japan in the post-war period, met Teigo Iba in his youth. Kawakami himself joined Sumitomo, attracted by Iba’s personality. Iba inspired great respect.

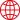
This photo was taken toward the end of the Taisho era at Restaurant Yanagiya in Ishiyama.
Photo courtesy of Sumitomo Historical Archives

 EN
EN




